This site includes free question papers for btech degree,study materials of bank,central govt jobs
Thursday, 29 October 2015
QA 6 SI AND CI
6 Simple Interest
It is the sum which is paid by the borrower to the lender for using the money for a specific time period. The money borrowed is called the Principal. The rate at which the interest is calculated on the principal is called Rate of Interest. The time for which the money is borrowed is Time and the total sum of principal and interest is called the Amount.
Simple Interest
Simple Interest
If P = Principal, R = Rate per cent per annum T = Number of years, SI = Simple Interest and A = Amount. Then,
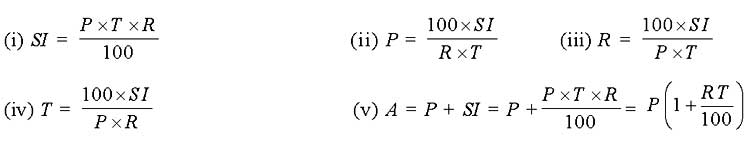
Here, the interest is calculated on the original principal ie, the principal to calculate the interest remains constant throughout the time period. The interest earned on the principal is not taken into account for the purpose of calculating interest for later years.
Compound Interest
In compound interest, the interest is added to the principal at the end of each period and the amount thus obtained becomes the principal for the next period. The process is repeated till the end of the specified time.
If P = Principal,
R = Rate per cent per annum
Time = Number of years,
CI = Compound Interest
A = Amount. Then,
When the interest is compounded annually
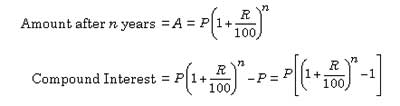
Important Formulae
1. If the rate of interest differs from year to year ie, R1 in the first year, R2 in the second year, R3 in the third year.
Then 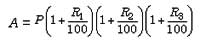
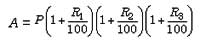
2. When the principal changes every year, we say that the interest is compounded annually. Then,
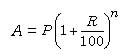
3. When the principal changes as per every six months, we say that the interest is compounded half yearly or semi-annually. Then,
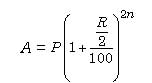
4. When the principal changes every three months, we say that the interest is compounded quarterly. Then,
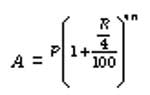
5. When the principal changes after every month, we say that the interest is compounded monthly. Then,
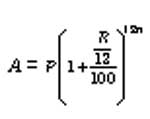
6. When the interest is compounded annually but time is in fraction say year.
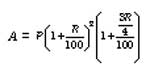
7. The difference between the simple interest and compound interest for 2 year (or terms) is given by the formula
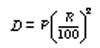
Where D is the difference, P is the principal and R is the rate of interest.
8. Present worth of x ` due n years, hence is given by
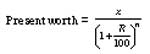
5 AVERAGE
5 Average
Average
The average of a given number of quantities of the same kind is expressed as
Average = Sum of the quantities/ Number of the quantities
Average is also called the Arithmetic Mean.
Average is also called the Arithmetic Mean.
Also, Sum of the quantities = Average × Number of the quantities
Number of quantities = Sum of the quantities/ Average
Number of quantities = Sum of the quantities/ Average
QA 4 Simplification
In simplification of an expression there are certain laws which should be strictly adhered to. These laws are as follows:
‘VBODMAS’ Rule
This rule gives the correct sequence in which the mathematical operation are to be executed so as to find out the value of a given expression. Here, ‘V’ stands for Vinculum (or Bar), ‘B’ stands for ‘Bracket’, ‘O’ stands for ‘Of’, ‘D’ stands for ‘Division’, ‘M’ stands for ‘Multiplication’, ‘A’ stands for ‘Addition’ and ‘S’ stands for ‘Subtraction’.
(1) Here, ‘VBODMAS’ gives the order of simplification. Thus, the order of performing the mathematical operations in a given expression are
- First : Vinculum or line bracket or bar
- Second: Bracket
- Third: Of
- Fourth: Division
- Fifth: Multiplication
- Sixth: Addition &
- Seventh: Subtraction
The above order should strictly be followed.
(2) There are four types of brackets.
- Square brackets [ ]
- Curly brackets { }
- Circular brackets ( )
- Bar or Vinculum –
Thus, in simplifying an expression all the brackets must be removed in the order ‘–’, ‘( )’, ‘{ }’ and ‘[ ]’.
Modulus of a Real Number
The modulus of a real number x is defined as = x, if a > 0
|x| = x, if a < 0
Basic Formulae
(i) (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2
(ii) (a – b)2 = a2 – 2ab + b2
(iii) (a + b)2 – (a – b)2 = 4ab
(iv) (a + b)2 + (a – b)2 = 2(a2 + b2)
(v) (a2 – b2) = (a + b) (a – b)
(vi) (a + b + c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2(ab + bc + ca)
(vii) (a3 + b3) = (a + b) (a2 – ab + b2)
- See more at: http://www.bankpoclerk.com/community/study-material/quantitative-aptitude/simplification#sthash.pikmd0V3.dpufAQA 3 HCF AND LCM
3 HCF AND LCM
Highest Common Factor
The highest common factor of two or more given numbers is the largest of their common factors. It is known as GCD also.
eg, Factors of 20 are 1, 2, 4, 5, 10, 20
Factors of 36 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18, 36
Here greatest and common factor of 20 and 36 is 4.
:-> HCF of 20 and 36 is 4.
Least Common Multiple
The least common multiple of two or more given numbers is the least of their common multiples.
eg, Multiple of 25 are 25, 50, 75, 100, 125, 150, 175, ..
Multiple of 30 are 30, 60, 90, 120, 150, 180, 210, ..
Here 150 is least common multiple of 25 and 30
:-> LCM of 25 and 30 is 150.
QA 2 SQUARE ROOTS
2 Square Root & Cube Root
Square Root
The square root of a number is that number the product of which itself gives the given number, ie, the square root of 400 is 20, the square root of 625 is 25.
The process of finding the square root is called evaluation. The square root of a number is denoted by the symbol called the radical sign.
How to Find the Square Root of an Integer?
(i) By the method of Prime Factors: When a given number is a perfect square, we resolve it into prime factors and take the product of prime factors, choosing one out of every two.
(ii) By the method of Long Division: This method can be used when the number is large and the factors cannot be determined easily. This method can also be used when we want to add a least number or to subtract a least number from a given number so that the resulting number may give a perfect square of some number.
- See more at: http://www.bankpoclerk.com/community/study-material/quantitative-aptitude/square-root-cube-root#sthash.f7eJyR8i.dpufstudy material of quantitaive aptitude in competative xams (bank ,ssc etc) 1 NUMBER SYSTEM
1 NUMBER SYSTEM
Place Value (Indian)
Face Value and Place Value of a Digit
Face Value: It is the value of the digit itself eg, in 3452, face value of 4 is ‘four’, face value of 2 is ‘two’.
Place Value: It is the face value of the digit multiplied by the place value at which it is situated eg, in 2586, place value of 5 is 5 × 102 = 500.
Place Value: It is the face value of the digit multiplied by the place value at which it is situated eg, in 2586, place value of 5 is 5 × 102 = 500.
Number CategoriesNatural Numbers (N): If N is the set of natural numbers, then we write N = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,…}
The smallest natural number is 1.
Whole Numbers (W): If W is the set of whole numbers, then we write W = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,…}
The smallest whole number is 0.
The smallest natural number is 1.
Whole Numbers (W): If W is the set of whole numbers, then we write W = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,…}
The smallest whole number is 0.
Integers (I): If I is the set of integers, then we write I = {– 3, –2, –1, 0, 1, 2, 3, …}
Rational Numbers: Any number which can be expressed in the form of p/q, where p and q are both integers and q # 0 are called rational numbers.
Rational Numbers: Any number which can be expressed in the form of p/q, where p and q are both integers and q # 0 are called rational numbers.
e.g. 3/2,7/9,5,2
There exists infinite number of rational numbers between any two rational numbers. Irrational Numbers Non-recurring and non-terminating decimals are called irrational numbers. These numbers cannot be expressed in the form of p/q .
e.g. √3, √5,√29
Real Numbers: Real number includes both rational and irrational numbers.
Basic Rules on Natural Numbers
1. One digit numbers are from 1 to 9. There are 9 one digit numbers. ie, 9 × 100.
2. Two digit numbers are from 10 to 99. There, are 90 two digit numbers. ie, 9 × 10.
3. Three digit numbers are from 100 to 199. There are 900 three digit numbers ie, 9 × 102.
In general the number of n digit numbers are 9 × 10(n–1)
2. Two digit numbers are from 10 to 99. There, are 90 two digit numbers. ie, 9 × 10.
3. Three digit numbers are from 100 to 199. There are 900 three digit numbers ie, 9 × 102.
In general the number of n digit numbers are 9 × 10(n–1)
Sum of the first n, natural numbers ie, 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + … + n = n n 1 / 2
Sum of the squares of the first n natural numbers ie. 12 + 23 + 32 + 42 + …+ n2 = n n 1 2n 1 / 6
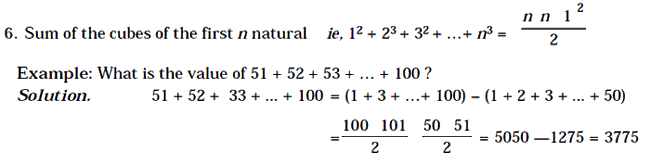
Different Types of Numbers
Even Numbers: Numbers which are exactly divisible by 2 are called even numbers.
eg, – 4, – 2, 0, 2, 4…
Sum of first n even numbers = n (n + 1)
Odd Numbers: Numbers which are not exactly divisible by 2 are called odd numbers.
eg, – 5, –3, –1, 0, 1, 3, 5…
Sum of first n odd numbers = n2
Prime Numbers: Numbers which are divisible by one and itself only are called prime numbers.
eg, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11…
eg, – 4, – 2, 0, 2, 4…
Sum of first n even numbers = n (n + 1)
Odd Numbers: Numbers which are not exactly divisible by 2 are called odd numbers.
eg, – 5, –3, –1, 0, 1, 3, 5…
Sum of first n odd numbers = n2
Prime Numbers: Numbers which are divisible by one and itself only are called prime numbers.
eg, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11…
- 2 is the only even prime number.
- 1 is not a prime number because it has two equal factors.
- Every prime number greater than 3 can be written in the form of (6K + 1) or (6K – 1) where K is an integer.
- There are 15 prime numbers between 1 and 50 and l0 prime numbers between 50 and 100.
Relative Prime Numbers: Two numbers are said to be relatively prime if they do not have any common factor other than 1.
eg, (3, 5), (4, 7), (11, 15), (15, 4)…
Twin Primes: Two prime numbers which differ by 2 are called twin primes.
eg, (3, 5), (5, 7), (11, 13),…
Composite Numbers Numbers which are not prime arc called composite numbers
eg, 4, 6, 9, 15,…
1 is neither prime nor composite.
Perfect Number: A number is said to be a perfect number, if the sum of all its factors excluding itself is
equal to the number itself. eg, Factors of 6 are 1, 2, 3 and 6.
Sum of factors excluding 6 = 1 + 2 + 3 = 6.
6 is a perfect number.
Other examples of perfect numbers are 28, 496, 8128 etc.
eg, (3, 5), (4, 7), (11, 15), (15, 4)…
Twin Primes: Two prime numbers which differ by 2 are called twin primes.
eg, (3, 5), (5, 7), (11, 13),…
Composite Numbers Numbers which are not prime arc called composite numbers
eg, 4, 6, 9, 15,…
1 is neither prime nor composite.
Perfect Number: A number is said to be a perfect number, if the sum of all its factors excluding itself is
equal to the number itself. eg, Factors of 6 are 1, 2, 3 and 6.
Sum of factors excluding 6 = 1 + 2 + 3 = 6.
6 is a perfect number.
Other examples of perfect numbers are 28, 496, 8128 etc.
Rules for Divisibility
Divisibility by 2: A number is divisible by 2 when the digit at ones place is 0, 2, 4, 6 or 8.
eg, 3582, 460, 28, 352, ....
eg, 3582, 460, 28, 352, ....
Divisibility by 3: A number is divisible by 3 when sum of all digits of a number is a multiple of 3.
eg, 453 = 4 + 5 + 3 = 12.
12 is divisible by 3 so, 453 is also divisible by 3.
eg, 453 = 4 + 5 + 3 = 12.
12 is divisible by 3 so, 453 is also divisible by 3.
Divisibility by 4: A number is divisible by 4, if the number formed with its last two digits is divisible by 4. eg, if we take the number 45024, the last two digits form 24. Since, the number 24 is divisible by 4, the number 45024 is also divisible by 4.
Divisibility by 5: A number is divisible by 5 if its last digit is 0 or 5.
eg, 10, 25, 60
eg, 10, 25, 60
Divisibility by 6: A number is divisible by 6, if it is divisible both by 2 and 3.
eg, 48, 24, 108
eg, 48, 24, 108
Divisibility by 7: A number is divisible by 7 when the difference between twice the digit at ones place and the number formed by other digits is either zero or a multiple of 7.
eg, 658
65 – 2 × 8 = 65 – 16 = 49
As 49 is divisible by 7 the number 658 is also divisible by 7.
eg, 658
65 – 2 × 8 = 65 – 16 = 49
As 49 is divisible by 7 the number 658 is also divisible by 7.
Divisibility by 8: A number is divisible by 8, if the number formed by the last 3 digits of the number is divisible by 8. eg, if we take the number 57832, the last three digits form 832. Since, the number 832 is divisible
by 8, the number 57832 is also divisible by 8..
by 8, the number 57832 is also divisible by 8..
Divisibility by 9: A number is divisible by 9, if the sum of all the digits of a number is a multiple of 9.
eg, 684 = 6 + 8 + 4 = 18.
18 is divisible by 9 so, 684 is also divisible by 9.
eg, 684 = 6 + 8 + 4 = 18.
18 is divisible by 9 so, 684 is also divisible by 9.
Divisibility by 10: A number is divisible by 10, if its last digit is 0. eg, 20, 180, 350,….
Divisibility by 11: When the difference between the sum of its digits in odd places and in even places is either 0 or a multiple of 11.
eg, 30426
3 + 4 + 6 = 13
0 + 2 = 2
13 – 2 = 11
3 + 4 + 6 = 13
0 + 2 = 2
13 – 2 = 11
As the difference is a multiple of 11 the number 30426 is also divisible by 11.
‘Smart’ Facts
- If p and q are co-primes and both are factors of a number K, then their product p x q will also be a factor of r. eg, Factors of 24 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12 and 24 prime factors of 24 are 2 and 3, which are co-prime also. Product of 2 × 3 = 6, 6 is also a factor of 24.
- If ‘p’ divides ‘q’ and ‘r’, then p’ also divides their sum or difference. eg, 4 divides 12 and 20. Sum of 12 and 20 is 32 which is divisible by 4. Difference of 20 and 12 is 8 which is divisible by 4.
- If a number is divisible by another number, then it must be divisible by each of the factors of that number. 48 is divisible by 12. Factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12. So, 48 is divisible by 2, 3, 4 and 6 also.
Division on Numbers
In a sum of division, we have four quantities.
They are (i) Dividend, (ii) Divisor, (iii) Quotient and (iv) Remainder. These quantities are connected by a relation.
(a) Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder.
(b) Divisor = (Dividend – Remainder) ÷ Quotient.
(c) Quotient = (Dividend – Remainder) – Divisor.
They are (i) Dividend, (ii) Divisor, (iii) Quotient and (iv) Remainder. These quantities are connected by a relation.
(a) Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder.
(b) Divisor = (Dividend – Remainder) ÷ Quotient.
(c) Quotient = (Dividend – Remainder) – Divisor.
Example 2: In a sum of division, the quotient is 110, the remainder is 250, the divisor is equal to the sum of the quotient and remainder. What is the dividend ?
Solution. Divisor = (110 + 250) = 360
Dividend = (360 × 110) + 250 = 39850
Hence, the dividend is 39850.
Solution. Divisor = (110 + 250) = 360
Dividend = (360 × 110) + 250 = 39850
Hence, the dividend is 39850.
Example 3: Find the number of numbers upto 600 which are divisible by 14.
Solution. Divide 600 by 13, the quotient obtained is 46. Thus, there are 46 numbers less than 600 which are divisible by 14.
Solution. Divide 600 by 13, the quotient obtained is 46. Thus, there are 46 numbers less than 600 which are divisible by 14.
Factors and Multiples
Factor: A number which divides a given number exactly is called a factor of the given number,
eg, 24 = 1 × 24, 2 × 12, 3 × 8, 4 × 6
eg, 24 = 1 × 24, 2 × 12, 3 × 8, 4 × 6
Thus, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12 and 24 are factors of 24.
• 1 is a factor of every number
• A number is a factor of itself
• The smallest factor of a given number is 1 and the greatest factor is the number itself.
• If a number is divided by any of its factors, the remainder is always zero.
• Every factor of a number is either less than or at the most equal to the given number.
• Number of factors of a number are finite.
• 1 is a factor of every number
• A number is a factor of itself
• The smallest factor of a given number is 1 and the greatest factor is the number itself.
• If a number is divided by any of its factors, the remainder is always zero.
• Every factor of a number is either less than or at the most equal to the given number.
• Number of factors of a number are finite.
Number of Factors of a Number: If N is a composite number such that N = am bn co... where a, b, c ... are prime factors of N and m, n, o ... are positive integers, then the number of factors of N is given by the expression (m + 1) (n + 1) (o + 1)
Example 4: Find the number of factors that 224 has.
Solution. 224 = 25 × 71
Hence, 224 has (5 + 1) (1 + 1) = 6 × 2 = 12 factors.
Solution. 224 = 25 × 71
Hence, 224 has (5 + 1) (1 + 1) = 6 × 2 = 12 factors.
Multiple: A multiple of a number is a number obtained by multiplying it by a natural number eg,
Multiples of 5 are 5, 10, 15, 20
Multiples of 12 are 12, 24, 36, 48
• Every number is a multiple of 1.
• The smallest multiple of a number is the number itself.
• We cannot find the greatest multiple of a number.
• Number of multiples of a number are infinite.
- See more at: http://www.bankpoclerk.com/community/study-material/quantitative-aptitude/number-system#sthash.fevrPXPf.dpufMultiples of 5 are 5, 10, 15, 20
Multiples of 12 are 12, 24, 36, 48
• Every number is a multiple of 1.
• The smallest multiple of a number is the number itself.
• We cannot find the greatest multiple of a number.
• Number of multiples of a number are infinite.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)